grub bootloader Configuration Changes
Kernel Boot Parameter Changes
Introduction
[edit]TODO: Expand introduction.
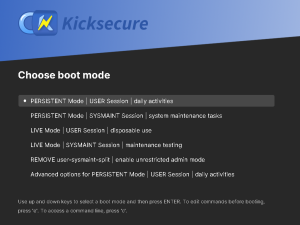
Figure: GRUB boot menu
Kernel Boot Parameters
[edit]Before trying specific kernel boot parameters, it is advisable to first add them temporarily for testing or troubleshooting purposes. When the parameters have the intended effect, they can then be added permanently.
Kernel boot parameters are text strings that disable/enable certain features or change specific system behaviors. To achieve the desired change, note kernel boot parameters: [1]
- can be a simple keywords (like "
splash" or "noapic") - are case-sensitive (for example "
Noapic" would not have any effect but "noapic" would take effect) - might have an
=sign to denote values (like "acpi_backlight=vendor") - might include punctuation (""
i8042.noloop")
Kernel boot parameters have no effect unless entered exactly as advised -- spelling/formatting errors or invalid values do not result in an error message.
Temporary Kernel Boot Parameter Change
[edit]Follow these steps to temporarily add and/or remove kernel boot parameters. Example use cases include:
- A) Enabling verbose boot messages for the purpose of debugging boot failures.
- B) Booting into Recovery Mode (single user mode).
- C) Testing kernel parameters temporarily before making them accessible through Permanent Configuration Changes.
- D) This list is far from exhaustive.
1. Restart the system. [2]
2. Access the grub menu.
Repeatedly press the ESC key until the grub menu appears. Alternatively, the shift key can be held down continuously for BIOS-mode (not UEFI-mode) until the menu appears. [3]
3. Change the GRUB keyboard layout.
Note: Optional.
Scroll all the way down using the ↓) until your reach Keyboard layout options. Press enter.
Navigate using the arrow keys (↑ or ↓ until you found your keyboard layout. Press enter.
Read the notice.
Switching keyboard layouts may cause the keyboard to malfunction or become unresponsive. If this occurs, force-reboot the machine to fix this. Keyboard layout `..` loaded. Press enter to continue.
Press enter to continue.
Press ESC to go back to the main menu.
Done.
Keyboard layout change complete.
4. Select the relevant entry to edit.
Use the arrow keys (↑ or ↓) to highlight the relevant entry and then press the e key to enter edit mode.
5. Go to the end of the line.
Use the arrow keys to move down to the line that contains boot arguments: [4]
- On BIOS systems, the line will begin with
linux. - On UEFI systems, the line begins with
linuxefi.
Press the end key to move the cursor to the end of that line.
6. Add or remove kernel boot parameter changes.
- A) Removing kernel parameters:
- Optional.
- For example, removing the following kernel parameters can be very useful for debugging:
loglevel=0quietrd.shell=0rd.emergency=halt
- And/or,
- B) Add kernel parameters: Press the space and carefully type in kernel boot parameter(s).
- Optional.
- For example, to enable Recovery Mode (single user mode), type: single
- Note: Replace
singlewith the actual kernel parameter.
7. Notes:
- Multiple parameters are separated with a
space. - No
spaces are added before/after any=(equals) signs or for punctuation in parameters.
8. Boot the system.
Press ctrl + X to boot the system with the new, temporary parameters.
9. Done.
The effect will only last for this boot session; once the system is restarted, they will no longer have any effect.
Permanent Configuration Changes
[edit]1. Learn how to configure permanent changes.
Inspect the following resources:
- folder
/etc/default/grub.d - file
/etc/default/grub.d/40_kernel_hardening.cfg
2. Create a new configuration file.
Open file /etc/default/grub.d/50_user.cfg in an editor with root rights.
Select your platform.
See Open File with Root Rights for detailed instructions on why using sudoedit improves security and how to use it.
Note: Featherpad (or the chosen text editor) must be closed before running the sudoedit command.
sudoedit /etc/default/grub.d/50_user.cfg
Notes:
- When using Kicksecure-Qubes, this must be done inside the Template.
sudoedit /etc/default/grub.d/50_user.cfg
- After applying this change, shut down the Template.
- All App Qubes based on the Template need to be restarted if they were already running.
- This is a general procedure required for Qubes and is unspecific to Kicksecure-Qubes.
Notes:
- This is just an example. Other tools could achieve the same goal.
- If this example does not work for you, or if you are not using Kicksecure, please refer to Open File with Root Rights.
sudoedit /etc/default/grub.d/50_user.cfg
3. Paste the necessary GRUB configuration change such as adding or removing kernel parameters.
Notes:
- The following example uses kernel parameter
nomodeset. - Replace only
nomodesetwith the actual kernel parameters you want to add. - Do not remove the leading text (underlined):
GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX="$GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX nomodeset". - Do not remove the trailing quote (
"; marked in bold):GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX="$GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX nomodeset".
GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX="$GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX nomodeset"
4. Save.
5. Regenerate grub configuration.
sudo update-grub
6. Done.
The process of adding a kernel parameter is complete.
7. Verification of GRUB configuration file.
Optional.
Inspect /boot/grub/grub.cfg because that is the generated file which is actually used during the boot process.
sudoedit /boot/grub/grub.cfg
8. Reboot.
A reboot is required for changes to take effect.
reboot
9. Verification of kernel command line
Inspect the virtual file /proc/cmdline.
cat /proc/cmdline
Inspect Grub Configuration Changes
[edit]1. Put folder /boot/grub under git version control.
Git is a useful tool to record which files in a folder changed in what way.
Git setup for folder /boot/grub.
Install package(s) git following these instructions
1 Platform specific notice.
- Kicksecure: No special notice.
- Kicksecure-Qubes: In Template.
2 Update the package lists and upgrade the system.
sudo apt update && sudo apt full-upgrade
3 Install the git package(s).
Using apt command line --no-install-recommends option is in most cases optional.
sudo apt install --no-install-recommends git
4 Platform specific notice.
- Kicksecure: No special notice.
- Kicksecure-Qubes: Shut down Template and restart App Qubes based on it as per Qubes Template Modification.
5 Done.
The procedure of installing package(s) git is complete.
Change directory to folder /boot/grub.
cd /boot/grub
Initialize git in that folder.
sudo git init
Git needs an e-mail address. That e-mail address doesn't need to actually exist. That e-mail address would appear in git commit change logs if that git repository was ever pushed to any remote. If only used locally, the default you@example.com could be kept. Otherwise, the user may change you@example.com to any e-mail address of their choice.
sudo git config user.email "you@example.com"
Git needs an name. That name address doesn't need to actually exist. That name would appear in git commit change logs if that git repository was ever pushed to any remote. If only used locally, the default Your Name could be kept. Otherwise, the user may change Your Name to any name of their choice.
sudo git config user.name "Your Name"
Add all files in that folder to git.
sudo git add -A
Commit all files to git. [5]
sudo git commit -a -m .
2. Change grub configuration.
Make changes according to Permanent Configuration Changes.
3. See which files were modified by update-grub.
From the same folder.
git status
4. Inspect the changes.
Using command line using default diff viewer diff which might be a bit difficult to read but an alternative is presented in the next step.
git diff
A graphical diff viewer can be used. Unspecific. Undocumented.
git difftool
Inspect Kernel Command Line
[edit]To view the kernel command line of the currently booted kernel, run.
cat /proc/cmdline
If too much output, use grep to filter.
Note: Replace parameter with the actual kernel parameter you are looking for.
cat /proc/cmdline | grep parameter
Goodies
[edit]- https://packages.debian.org/trixie/grub-image-boot

- https://packages.debian.org/trixie/grub-customizer

Boot with Manual Commands
[edit]TODO: document
https://forums.kicksecure.com/t/kicksecure-no-password-prompt-on-gnu-grub/483/3![]()
Boot Related Screenshots
[edit]TODO: document
GRUB Bootloader Authentication Password Prompt
[edit]Notes:
- This is an authentication password for the GRUB bootloader, providing basic protection against unauthorized access. It is unrelated to Full Disk Encryption.
- This is for protecting GRUB menu and settings from unauthorized changes.
Refer to:
Figure: GRUB Bootloader Authentication Password Prompt
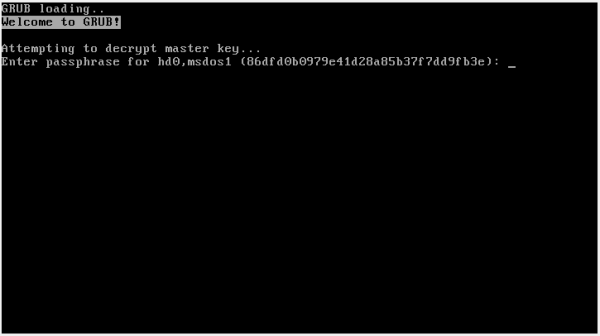
Legacy BIOS - GRUB Bootloader Disk Decryption Password Prompt
[edit]Figure: GRUB Bootloader Disk Decryption Password Prompt for (Legacy BIOS)
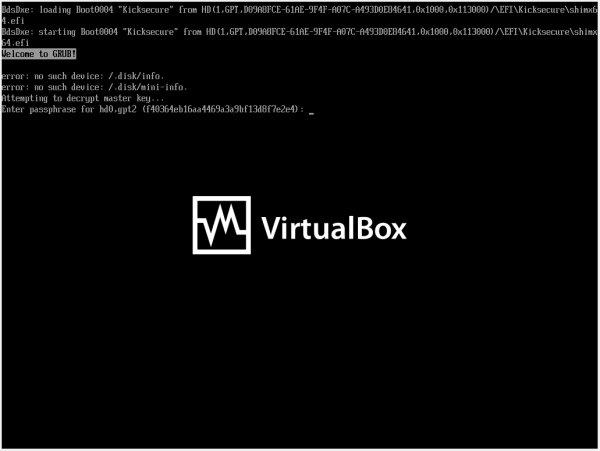
EFI - GRUB Bootloader Disk Decryption Password Prompt
[edit]Figure: GRUB Bootloader Disk Decryption Password Prompt (EFI)
EFI - SecureBoot - Boot Error Message
[edit]This is a known issue. No bug report is required.
Figure: EFI SecureBoot Boot Error Message
To resolve this issue, refer to Secure Boot.
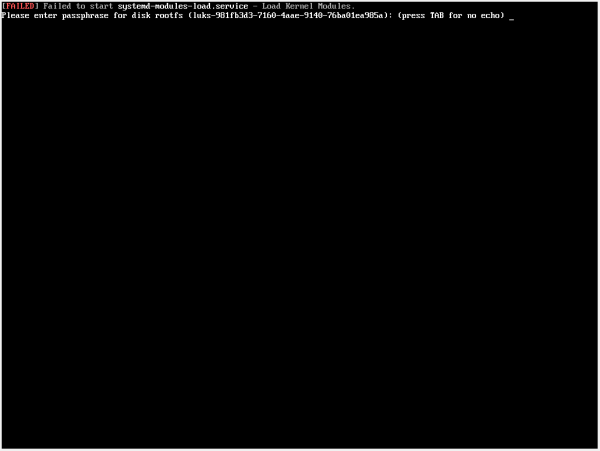
initramfs (initramfs-tools or dracut) Based Encryption Password Prompt
[edit]Please enter passphrase for disk ... (press TAB for no echo)
Figure: initramfs (initramfs-tools or dracut) Based Encryption Password Pre-Boot Authentication Prompt - Example (cropped)
Figure: initramfs (initramfs-tools or dracut) Based Encryption Password Prompt - Example (full)
This is related to Full Disk Encryption (FDE).
The installer currently requires that you set a disk encryption passphrase when you’re on the “Partitions” screen. Whatever passphrase you set at that point, type that in and press “Enter”. If you don’t remember entering a passphrase, but do remember entering a password at some point, type in that password."Please enter passphrase for disk rootfs" message
Kicksecure Specific
[edit]Screenshots
[edit]/etc/default/grub.d/20_dist-base-files.cfg
[edit]File /etc/default/grub.d/20_dist-base-files.cfg
Technical information:
For advanced users only. Laymen users an skip this additional explanation. See /etc/default/grub.d/20_dist-base-files.cfg.
See Also
[edit]Footnotes
[edit]- ↑
https://wiki.ubuntu.com/Kernel/KernelBootParameters

- ↑ Or shut it down and power it on again.
- ↑ The system might hang when holding down the shift key. If that happens, just briefly release the shift key and hold it down again until the grub menu appears.
- ↑
https://web.archive.org/web/20220312140233/https://docs.fedoraproject.org/en-US/Fedora/22/html/Multiboot_Guide/GRUB-runtime.html

- ↑
Commits all files to git with commit message
.for simplicity. Commit message could also be something else such as{{{sudo_maybe}}} git commit -a -m "initial commit".

We believe security software like Kicksecure needs to remain Open Source and independent. Would you help sustain and grow the project? Learn more about our 13 year success story and maybe DONATE!